AI in Healthcare Specialization - Introduction to Healthcare¶
Ai In Healthcare¶
Introduction To Healthcare¶
Module 1¶
Overview And Key Challenges¶
Q: Describe the differing interests of patients, intermediaries and providers.
Answer:
Remarks:
Q: What are the two types of intermediaries?
Answer:
Q: How do we call people who have an insurance policy?
Answer: They are called
of the insurance policy.
Q: What are the three key challenges of health care systems?
Answer:
Q: Which four reasons for rising healthcare costs do the instructors list?
Answer:
Q: Draw an updated version of the simple interaction between providers and patients, now including intermediaries.
Answer: 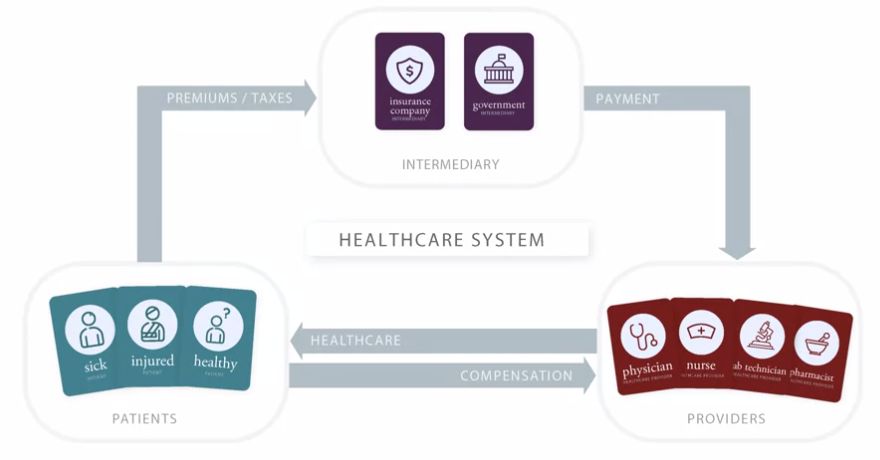
Q: What are intermediaries?
Answer: The course instructors define intermediaries as entitities that collect funds from a group of people, pool the funds, and use them to pay for healthcare for the people who are covered.
Remarks:
Q: What does it mean when we say many physicians work in outpatient settings?
Answer: By outpatient setting, we generally mean outside of a hospital.
Example: For example, they may work in a physician office or a clinic (referred to as a physician surgery in some places).
Remarks:
Q: What is an insurance policy?
Answer:
Q: Draw an image of the simple interaction between providers and patients.
Answer: 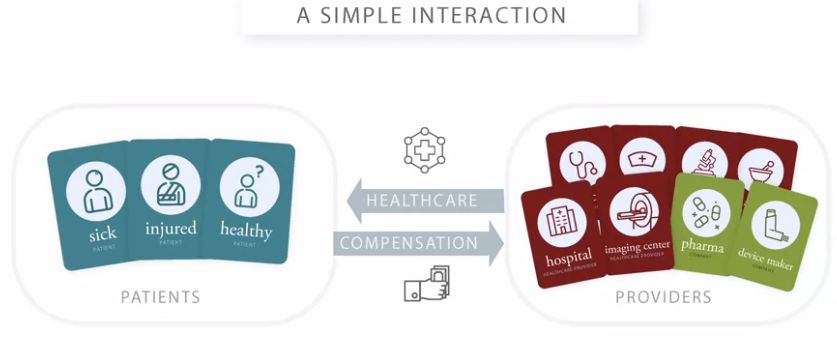
Q: What is a solution to the problem of risk?
Answer: Risk pooling
Q: What is risk pooling?
Answer: The instructors define risk pooling as the spreading of financial risks across a large number of contributors to a pool, so that the level of risk facing any one person is reduced by combining risks across multiple people.
Remarks:
Q: What is a premium?
Answer: It's the price charged for an insurance policy.
Q: How do the instructors define risk?
Answer:
Q: What are insurance companies?
Answer:
Remarks:
Q: What are some of the access challenges of healthcare?
Answer:
Q: Describe the different levels of care.
Answer:
Q: What does it mean when we say some physicians work in inpatient settings?
Answer:
Module 2¶
Physician Practices And Physician Payments¶
Q: Which incentives are generated by FFS payment systems and what are associated risks?
Answer:
Q: What is Medicare?
Answer: It is the US government payer that provides coverage for people mainly over the age of 65.
Q: Which incentives are generated by capitation payment systems and what are associated risks?
Answer:
Q: What is Fee for Service (FFS) payment?
Answer: In this payment model, a doctor is paid for each service that she or he provides.
Q: Explain how capitation payments can lead to a shift of risk from the intermediary to the provider.
Answer:
Q: What are the three challenges for the quality of healthcare?
Answer:
Q: How do the instructors define capitation payment?
Answer: It is defined as a payment system in which a physician is payed a fixed amount per patient, per unit of time.
Remarks: This can be seen as the opposite from FFS payment.
Module 3¶
Hospitals And Payment Systems¶
Q: What is an integrated delivery network (IDN)?
Answer: It is an entity that owns, or closely integrates, many providers of different types to provide a broad range of care.
Q: What are admitting privileges?
Answer: These are arrangements for physicians to provide services at a hospital.
Remarks: In this case, physician practice and hospital are still separate businesses and probably paid separately.
Q: What is a hospital network?
Answer: It is a group of hospitals with whom an insurer works, and which enrollees are required or encouraged to use.
Q: What is the global budget model?
Answer: It is a payment system for inpatient care, where the hospital is paid a fixed amount for a period of time (often a year).
Q: What are physician-hospital organizations (PHO's)?
Answer: These are larger organizations consisting of many hospitals that are part of the same company.
Q: What is pay-for-performance (P4P)?
Answer: It is the use of financial incentives or penalties based on whether or not a provider meets some set of performance expectations (focused on the quality of care).
Q: What is a personal health record (PHR)?
Answer: It commonly refers to an electronic application for patients to record their own personal health information.
Remarks: This may be for the patients' own use or to share with their healthcare providers.
Q: What are Diagnosis-Related Groups (DRG)?
Answer: It is a payment system where hospitals are paid a flat amount for each patient's hospital stay based on the given diagnosis.
Q: How can FFS, Per diem, DRG and Global budget systems be arranged according to the amount of risk transferred from intermediaries to hospitals?
Answer: They can be arranged from less risk to most risk transferred according to:
Q: What are hospital systems?
Answer: These are larger organizations consisting of many hospitals that are part of the same company.
Q: How do we call large PHO's with a broader representation of physicians?
Answer: We then apply the term: integrated delivery network (IDN).
Q: What is an Accountable Care Organization (ACO)?
Answer: It is an organization that works to create clinical integration (providers work together to deliver integrated and coordinated patient care) across many providers.
Remarks: Here, each provider or organization can voluntarily associate with the ACO, have some contractual arrangements, but stay in their own separate
organization.
Q: What is a chargemaster of a hospital?
Answer: It is a list of all the services that a hospital provides, and the amount that the hospital charges for each service.
Q: How does per diem payment work?
Answer: In a per diem payment system intermediaries pay a fixed amount to the hospital for each patient per day.
Remarks: This payment is a prospective payment since it does not regard the actual hospital's charges incurred for the provided services.
Q: What is a defining characteristic of a hospital?
Answer: The provision of beds and infrastructure for inpatient care.
Q: What are the two kinds of relationships between hospitals and physicians?
Answer:
Q: Which are the four payment systems for hospitals?
Answer:
Q: How can FFS, Per diem, DRG and Global budget systems be arranged according to incentives they create?
Answer: They can be arranged according to the incentive they create to provide care from most care to least care in the following way:
Remarks: More care can lead to overuse, less care can lead to underuse!
Q: What is an electrical medical record (EMR)?
Answer: It is a digitized version of a patient's medical record.
Q: What are hospitals?
Answer: They are organizations that provide facilities and staff to offer medical care.
Remarks: They can operate as
private businesses, on a for-profit or a not-for-profit basis, and some hospitals are owned or operated by governmet organizations.
Module 4¶
Intermediaries And Health Care Financing¶
Q: What are the five tools that intermediaries can use to influence health care use and spending?
Answer:
Q: What is a network provider panel?
Answer: It is the set of providers organized by an intermediary to care for enrolled patients.
Q: What is selective contracting?
Answer: It is the selection of only a subset of providers into the intermediaries' network.
Q: How do closed, open, and semi-open/semi-closed panels differ from each other?
Answer:
Q: What are the three common health plan designs?
Answer:
Example:
Q: What is "managed care"?
Answer: A health plan design is defined as “managed care” if the intermediary aims to manage the
care of its enrollees through the use of the intermediary tools.
Example: Examples are HMOs and PPOs.
Module 5¶
Healthcare Products And Prescription Drugs¶
Q: Which are the two main groups of drugs?
Answer:
Remarks: Prescription drugs require a prescription to obtain them, while over-the-counter drugs do not.
Q: Sketch the steps a prescription drug has to go through in order to get approval by the FDA.
Answer:
Remarks: It takes a long time for drug approvals; 9 years is a general estimate number and it can cost many millions or even billions of dollars.
Q: What is the difference between branded drugs and generic drugs?
Answer:
Remarks: Branded drugs tend to be more expensive. When generic drugs enter the market, competition drives down the price.
Q: What's the formulary?
Answer: It is a list of drugs that a patient can buy and then get reimbursed for it.
Q: What can a pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) do?
Answer:
Q: What is a pharmacy switch?
Answer: It is a third-party vendor used by pharmacists to transmit claims from the pharmacy to the PBMs.
Remarks:
Q: What are the six domains of quality?
Answer: